Study reveals staggering toll of being Black in America: 1.6 million excess deaths over 22 years
By Liz Szabo, KFF Health News
May 16, 2023
 Racism is at the heart of the American government’s failure to tackle the growing threat of deadly heatwaves, according to the author of an authoritative new book on the heating planet.
Racism is at the heart of the American government’s failure to tackle the growing threat of deadly heatwaves, according to the author of an authoritative new book on the heating planet.
Research has long shown that Black people live sicker lives and die younger than white people.
Now a new study, published Tuesday in JAMA, casts the nation’s racial inequities in stark relief, finding that the higher mortality rate among Black Americans resulted in 1.63 million excess deaths relative to white Americans over more than two decades.
Because so many Black people die young — with many years of life ahead of them — their higher mortality rate from 1999 to 2020 resulted in a cumulative loss of more than 80 million years of life compared with the white population, the study showed.
Although the nation made progress in closing the gap between white and Black mortality rates from 1999 to 2011, that advance stalled from 2011 to 2019. In 2020, the enormous number of deaths from Covid-19 — which hit Black Americans particularly hard — erased two decades of progress.
Authors of the study describe it as a call to action to improve the health of Black Americans, whose early deaths are fueled by higher rates of heart disease, cancer, and infant mortality.
“The study is hugely important for about 1.63 million reasons,” said Herman Taylor, an author of the study and director of the cardiovascular research institute at the Morehouse School of Medicine.
“Real lives are being lost. Real families are missing parents and grandparents,” Taylor said. “Babies and their mothers are dying. We have been screaming this message for decades.”
High mortality rates among Black people have less to do with genetics than with the country’s long history of discrimination, which has undermined educational, housing, and job opportunities for generations of Black people, said Clyde Yancy, an author of the study and chief of cardiology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine.
Black neighborhoods that were redlined in the 1930s — designated too “high risk” for mortgages and other investments — remain poorer and sicker today, Yancy said. Formerly redlined ZIP codes also had higher rates of Covid infection and death. “It’s very clear that we have an uneven distribution of health,” Yancy said. “We’re talking about the freedom to be healthy.”
A companion study estimates that racial and ethnic inequities cost the U.S. at least $421 billion in 2018, based on medical expenses, lost productivity, and premature death.
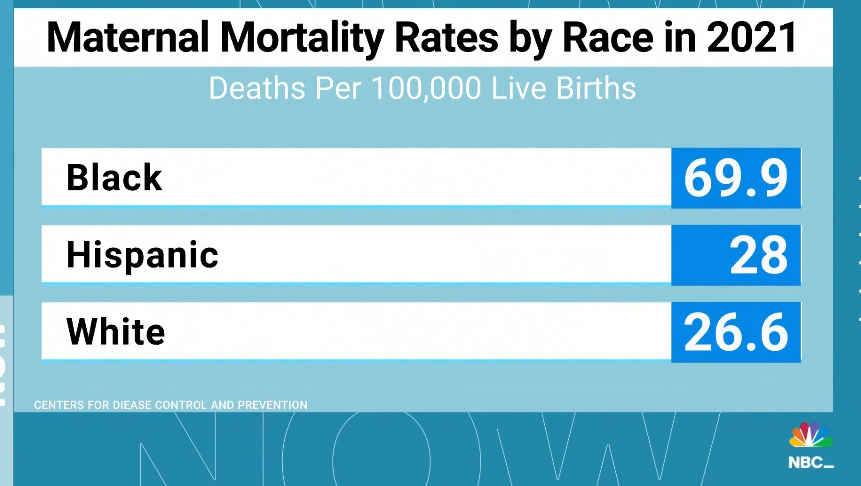
In 2021, non-Hispanic white Americans had a life expectancy at birth of 76 years, while non-Hispanic Black Americans could expect to live only to 71. Much of that disparity is explained by the fact that non-Hispanic Black newborns are 2½ times as likely to die before their first birthdays as non-Hispanic whites. Non-Hispanic Black mothers are more than 3 times as likely as non-Hispanic white mothers to die from a pregnancy-related complication. (Hispanic people can be of any race or combination of races.)
Racial disparities in health are so entrenched that even education and wealth don’t fully erase them, said Tonia Branche, a neonatal-perinatal medicine fellow at Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago who was not involved in the JAMA study.
[READ FULL ARTICLE HERE]
